1.What is Antiphospholipid Syndrome?
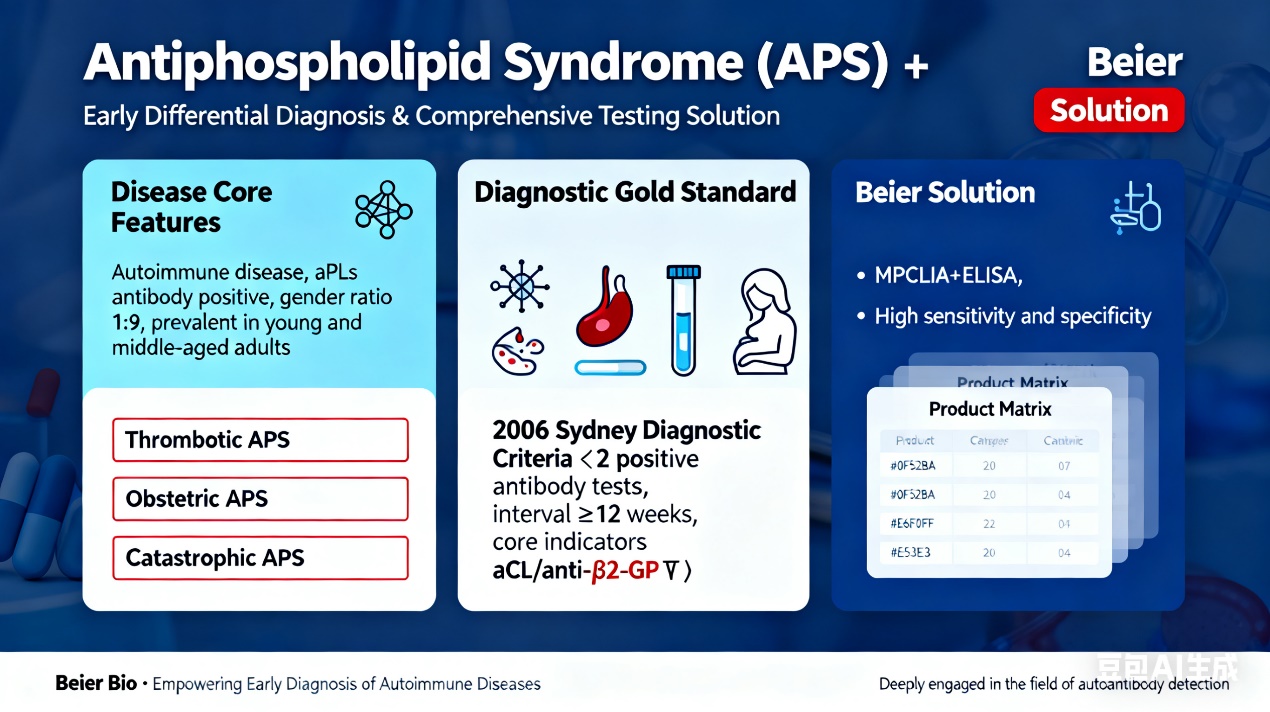
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by recurrent vascular thrombotic events, recurrent spontaneous abortion, thrombocytopenia, and other major clinical manifestations, accompanied by persistent moderate to high positivity of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs). Its clinical manifestations are complex and diverse, involving multiple organ systems throughout the body. Clinically, Thrombotic APS and Obstetric APS are the most common subtypes. APS predominantly affects females, with a male-to-female incidence ratio of approximately 1:9, and is more prevalent in young and middle-aged adults. It is generally classified into Primary APS (PAPS) and Secondary APS (SAPS). The latter is mostly secondary to connective tissue diseases (CTDs) such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), and currently accounts for the majority of APS cases.
2.Clinical Manifestations of Antiphospholipid Syndrome
The manifestations and symptoms of APS are closely associated with pathological thrombosis, which vary depending on the size and location of the thrombus. Thrombi can form locally or migrate through the circulation to the arteries and veins of the brain, heart, kidneys, lungs, and extremities, leading to slowed blood flow or even occlusion. This may result in organ damage, failure, and potentially death.
APS is also associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, including recurrent abortion, mid-to-late trimester miscarriage, or preterm birth caused by preeclampsia. In rare cases, some APS patients may develop multiple blood clots within weeks or months, a life-threatening condition known as Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome (CAPS).
As proposed by the expert panel at the 2006 Sydney Revised Classification Criteria for APS, APS may present with aPLs-related clinical manifestations beyond thrombotic events and adverse pregnancy outcomes. These include livedo reticularis, superficial thrombophlebitis, thrombocytopenia, aPLs-related renal lesions, cardiac valve lesions (e.g., valvular vegetations, thickening, and regurgitation), hemolytic anemia, chorea, cognitive impairment, and transverse myelitis. Unlike vascular thrombotic events, these manifestations are often linked to the procoagulant or proinflammatory effects of aPLs and are commonly referred to as “extra-classification criteria manifestations.” They are closely associated with the risk of thrombotic events, adverse pregnancy outcomes, and disease prognosis, providing additional diagnostic value and potentially influencing treatment decisions.
3.Detection Methods for Antiphospholipid Syndrome
The management of APS primarily focuses on treating the underlying disease, with the main goals of reducing thrombotic events and preventing pregnancy failure. Detection of APS-related antibodies exhibits high disease specificity; early detection can predict the occurrence of the aforementioned symptoms. Therefore, early diagnosis and rational treatment are crucial for both patients with Thrombotic APS and Obstetric APS. When relevant clinical manifestations occur, aPLs testing should be performed promptly.
According to the 2006 Sydney Revised Classification Criteria for APS, the diagnosis requires the detection of moderate to high titers of anticardiolipin (aCL) IgG or IgM antibodies (≥40 GPL/MPL units, or at or above the 99th percentile of healthy controls) or anti-β2-glycoprotein Ⅰ (anti-β2-GPⅠ) IgG or IgM antibodies (at or above the 99th percentile of healthy controls) on two or more occasions, separated by at least 12 weeks.
4.Beier Bio Provides a Comprehensive Testing Solution for the Early Differential Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome
With years of expertise in the field of autoantibody detection, Beier Bio offers testing technologies covering ELISA and CLIA, featuring high sensitivity and specificity. The company provides a comprehensive testing solution for the early differential diagnosis of APS, with the following products:
|
PRODUCT NAME |
|
| 1 | Anticardiolipin IgG ELISA Kit |
| 2 | Anti-β2-GP1 IgG ELISA Kit |
| 3 | Anticardiolipin IgM Detection Kit (CLIA) |
| 4 | Anticardiolipin IgG Detection Kit (CLIA) |
| 5 | Anticardiolipin IgA Detection Kit (CLIA) |
| 6 | Anticardiolipin Antibodies Detection Kit (CLIA) |
| 7 | Anti-β2-GP1 IgM Detection Kit (CLIA) |
| 8 | Anti-β2-GP1 IgG Detection Kit (CLIA) |
| 9 | Anti-β2-GP1 IgA Detection Kit (CLIA) |
Post time: Oct-21-2025